Redness, peeling of the skin on the legs, the appearance of cracks between the fingers, the gastric ulcer on the feet, a change in the condition of the nails: loss of gloss, the usual pink shade, thickening of the plates - these and other signs indicate the development of a fungal infection. Every fifth resident of the earth is sick of mycosis. Therefore, you need to know what the fungus looks and behaves on the legs, what causes leader to its appearance and how to treat this unpleasant disease.
Causes
In most cases, infection of mycose comes from a person to a person directly or through the surrounding objects. Favorable conditions for reproduction of the fungus are fever, humidity. Disputes can also maintain the viability of a dried state after poor quality treatment of manicure tools.
The main reasons for the disease include:
- Lack of regular feet.
- Accommodation with a person suffering from a sponge.
- Using someone else's shoes, socks.
- Stop Damage.
- Visit "mushrooms" common areas (beaches, baths, pools).
- Insufficient treatment of pedicyr accessories.
- Wearing tight shoes from synthetic materials.
- Professional harmfulness (work under high temperature and humidity conditions).
- Shooting shoes in a store without a sock or a detachment.
Fungal diseases in humans develop faster based on the functions of function, as well as changes leading to the oppression of immunity, decreased local circulation, changes in the condition of the skin. The causes of the body are as follows:
- Endocrine pathology (diabetes, obesity);
- pregnancy;
- Immunodeficiency says;
- Increased sweat;
- Foot diseases;
- vascular disorders;
- chronic skin diseases (eczema, psoriasis);
- Long -term intake of drugs that suppress immunity (corticosteroids, cytostatics).
Types of pathogenic mushrooms
Mushrooms on the human body live on proteins - keratin, elastin, collagen, divide them with enzymes: keratinase. The location of mycose depends on the activity of the keratinase and the ability to digest different types of keratin.
Mycoses on the legs causing the following types of mushrooms:
- Trichophyton Rubrum-a type of fungal saprophytes that inhabit a keratinized skin layer. Causes of cutting low, damage to the epidermis, nails in 80 % of cases.
- Trichophyton -Tentaphyhytes cause stop epidermophytius.
- Trichophyton Interdigital. On the legs, the fungus causes dermatophytosis, onychomycosis.
- Mushrooms in the genus Candida affect the skin, and the nail plates with a severe decrease in immunity affect the skin and nail plates with a severe decrease in immunity.
Mushroom skin lesions
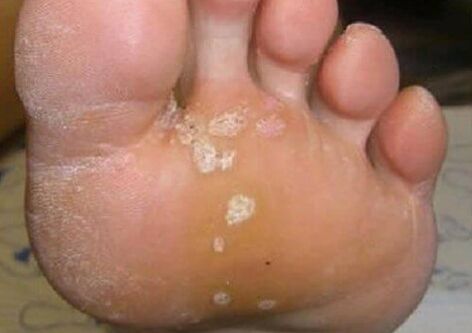
From mycosis on the legs, lesion of the skin during psoriasis (sometimes it is called a dry sponge) - red plaques with peeling and a tendency to merge increasing over the surface. Such elements are often found on the knees, legs. This disease is not associated with a fungal infection.
The manifestations of the foot fungus are conditionally divided into four main forms. Convention is in a combination of clinical signs and the possibility of transition apart.
In intertriginous form, the skin suffered in interdigital spaces. The fungus on the skin on the legs manifests in the form of itching, burning, it is accompanied by an unpleasant odor. Often, the infection affects the foot from intervals between 3 and 4, 4 and 5 fingers. The skin becomes red, impregnated with moisture, wounds, crying areas appear between the fingers. These characters develop independently or on the basis of an existing plate -shaped form.
Note! For intertriginous lesion is typically the attachment of a secondary bacterial infection that aggravates the disease. Bacterial, mycotic eczema develops with the formation of a rash, not only on the foot, inflammatory elements appear on the ankle and lower.
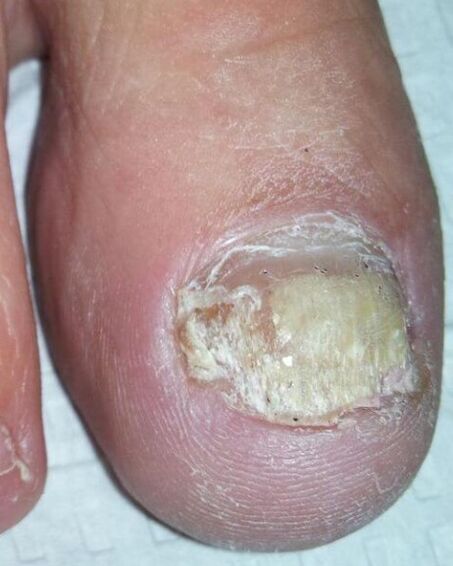
The advanced plate-hyperkeratotic shape is similar to ordinary, massive corn on the sole of cracks. Originally, mycose of the skin on the legs can attract attention with dryness, peeling of the feet, limited rough corn on the heels. People consider such symptoms as an individual function and do not turn to a dermatologist. Skin lesions can accompany itching, burning. If you look at the images of the fungus on the legs with this kind of mycose, you may notice deep cracks based on a thickened (and as it was, shut down in moccasins) of the feet. Such manifestations are painful. The plate shape is characterized by the involvement of nail plates with their destruction, a delay behind the nail bed.
The manifestations of the dyshidrotic (vesicular) form of the foot fungus are rare. The biggest symptom of the disease is the formation of bubbles with a thick shell and transparent content. They are located on the only side of the foot, fingers as simple or drainage formations. Then the bubbles are opened with the formation of erosion with purulent crust around the edges. Complications of vesicular lesion include:
- Toxic-allergic reactions. They develop for 4-6 days, often localized symmetrical: swollen reddish papules are found on the foot, lower leg, forearm, face, mucous membranes.
- Connection of a secondary bacterial or viral infection with the development of eczema.
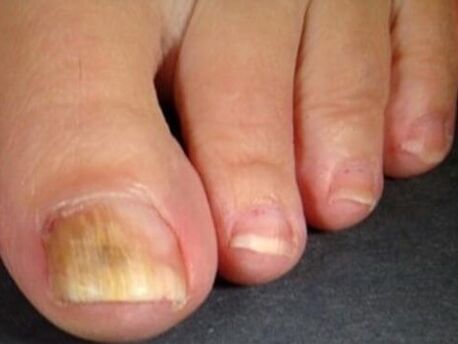
The erased form of the fungus on the feet is characterized by minimal lesions, so it is not easy to recognize it. The most important signs: the appearance of intestinal peeling, the formation of microcracies between the fingers, the discomfort, the burning. With a long course, the nail plates are involved.
Nail sponge
Onychomycosis occurs as a result of the skin fungus on the fingers, feet, in the absence of attention to the problem and adequate treatment.
The first symptoms and signs of onychomycosis can also go unnoticed. You should contact the nail sponge on the legs and contact a dermatologist at:
- Change in the color of the nail plates;
- the appearance of yellow or grayish spots;
- Loss of luster;
- Appearance on the surface of irregularities;
- Strips in the nail structure;
- Increased Britidness.
There are different classifications of onychomycosis. At the appearance of the nail plate, they are divided into:
- Normotrophic. The fungal infection changes the color of the nails to yellow -gray, the thickness and the mold remains the same.
- Hypertrophic. This type of fungus is characterized by coarse changes: the nails turn yellow, thicker. If you look at the photos showing this type of onychomycosis, you may notice a distinctive choracible form of the plates. Cross -cutting studies, solution and gap at the free edge are visible. Such a change in nails leads to their growing. Walking becomes painful.
- Onycholithic. The nail plates become thinner, change color, exfoliates from the nail bed.
According to the location and degree of damage to the nail plate, the following types of onychomycosis are separated: distal; lateral; mixed, proximal; total; surface.
Candidiasi's defeat
Separately, the damage to the mushrooms in the genus Candida should be considered. These conditional pathogenic fungi cause deep (affect internal organs) and surfaces mycoses (dermatomycosis, onychomycosis). Under normal conditions, human immunity suppresses the reproduction of this fungus and a massive infection does not occur. Therefore, the activity of Candida is manifested with significant disorders in the body of protecting the body and requires a thorough examination to establish the cause of immunodeficiency. The first signs of infection are difficult to distinguish from damage, frostbite.
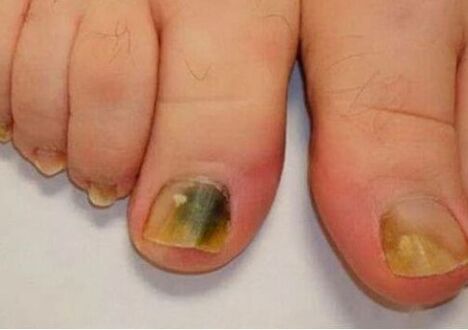
The fungal damage on the legs develops as follows:
- On the fingers of the legs there is an inflammation of the nail rolls with redness, swelling, cracks on the skin, the appearance of discomfort in any movements. Under the nail plates, a purulent is formed separated whitish shade.
- Inflammatory changes in the skin fall down, the disease becomes chronic. The skin around the nail thickens, stops growing. The infection affects the nail plates.
- The nails on the legs begin to thicken, to sprinkle. Their color turns brown, brown. Violation of the blood supply leads to rejection.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the fungus on the legs includes:
- Conversation with the patient (complaints, accompanying illnesses, working conditions, clarification of the possibility of infection).
- Inspection.
- Laboratory research methods (scraping of the skin, nails with microscopy, sowing a dedicated crop with the determination of sensitivity to drugs, IG g to Aspergille, candidates).
Treatment
The fungus on the legs requires immediate treatment, as a dermatologist (or mycologist) will prescribe. You can perform tasks on an outpatient basis.
How and how to treat the fungus on the legs depends on a number of conditions:
- Localization of the pathological process;
- degree, the severity of defeat;
- the presence of contemporary diseases;
- Patient age;
- In the case of therapy of women - the fact of pregnancy, breastfeeding.
Treatment of the fungus on the legs takes a lot of time and its main target is the disappearance of clinical and laboratory events on infection. An incomplete course of treatment leads to relapse of the disease.
Drug therapy
Pharmaceutical treatment is performed using antifungal drugs that not only destroy mycosis but also help remove the manifestations of inflammation and eliminate the secondary infection.
They are divided into:
- Local. Apply to the lesion (ointment, gel, cream, spray, varnish, solution).
- Systemic - Take orally (tablets, capsules, solutions).
At the initial step of a fungal infection, drug therapy is limited to the appointment of local funds. With ordinary mycose, with a serious course, the connection between systemic antimycotics is required.
Treatment with folk remedies.
There are many recommendations on how to get rid of the fungus on the legs of folk and home medicine. Most involves external use and some - inward. However, you should not drink and apply questionable compositions to your feet hoping to bring the neglected mycosis. Such folk methods can harm health.

Note! The most common and effective homemaker for fungus is the legs of legs with salt, soda, essential oils. These therapeutic procedures prepare feet and nails for the use of medications.
Surgical treatment
With a massive fungal damage, the nail plates must be removed. This method is safe and has virtually no contraindications. An alternative to surgical manipulation - the use of pastes and ointments to soften nails followed by removal.
Laser treatment
The use of a laser for fighting onychomycosis is based on the heating and destruction of the spores of the fungus with a directed beam. This technique allows you to quickly cure onychomycosis, safe and applicable in patients contraindicated in systemic treatment.
Treatment of dermatomycosis
To start the treatment of the fungus, local antifungal agents are used on the legs. If, after a 2-week course of treatment, there is no improvement in the condition, an antimycotic agent is required. In case of serious injury, skin fungus requires a prescription for systemic drugs. Therapy continues until the complete elimination of the infection.
Treatment of onychomycosis
To eliminate the initial manifestations of Nail Fungus, local drugs are prescribed. Mycosis with a lesion of more than 2/3 of the nail area involving growth zone, distribution to other plates - an indication of taking systemic drugs. Onychomycosis with massive destruction of the nail plates begins to be treated with surgical removal of the affected tissue in the nail. This method provides access to focus on infection.
Important!
Treatment of onychomycosis is performed before growing healthy nails and can last up to 12 months.
The appearance of the fungus on the legs may be caused by different reasons. An attentive attitude towards your health will help recognize the disease in time and begin treatment.